Topic 6 Review Questions Money Banking and Financial Markets Answers
Money, Banking and the Fiscal Sector
At the terminate of this chapter you should empathize
-
How the fiscal system is represented in the economy
-
The cardinal depository financial institution lending rate and the policy rate
-
Credit rationing and data asymmetries
-
Bank liquidity, solvency and the balance sheet

Banking concern
This chapter is about the function of money and cyberbanking in the macro economy. This subject field has been ignored in some macroeconomic models. Models such as the Real Business Wheel assume that the financial system operates smoothly without whatever frictions. If the system is working well, economic agents can carry out their planned expenditure using coin and credit. Even so, the Global Financial Crunch (GFC) made articulate the disruption that may be felt when the financial arrangement is not working well.
At that place are two new features introduced to the model when nosotros expect more than closely at the financial organisation:
-
There is a distinction between the policy rate and the lending charge per unit;
-
Banks intermediate between depositors and borrowers and impose borrowing constraints on some parties (credit rationing);
Banking mark-upwardly
Upwardly to now the central bank has been able to set the involvement charge per unit to obtain the level of economic activity that is required. However, information technology is necessary to distinguish between the banking concern rate and the lending rate that is set by financial institutions. It is the lending charge per unit that is important for economical amanuensis financial decisions. The lending rate is the mark-up on the policy rate that is determined by the banks' optimising decisions. For the IS bend, we now take the lending rate on the y-centrality and denote the Policy charge per unit as that set by the primal bank. The difference between the 2 is banking mark-up. This allows an analysis of shocks to the banking system that tin can widen the spread.
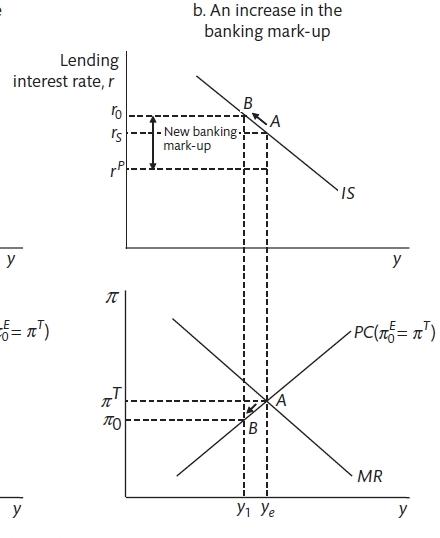
The Cyberbanking Mark-up (Carlin and Soskice 2015)
If in that location is a daze to the cyberbanking organization unanticipated by the central banking company that results in an increment in the margin that banks accuse higher up the policy charge per unit (perchance because they become more concerned about bad loans), this will cause an unanticipated shift forth the IS curve and will push the economy below the stabilising level of output. In these cases, the primal bank must cut interest rates to reduce the lending charge per unit and bring output back to the stabilising level.
Coin and the macroeconomic
Coin has three functions:
- Means of transaction. It is used to buy things. There is no demand to castling. The more transactions the more money that is required.
- Unit of account. It allows comparison. If the value of money changes chop-chop, it is hard to use for comparison.
- Store of value. Information technology is used for savings. If it loses value it is not useful for saving.
Households select the amount of greenbacks that they want to concur. This will be determined past their desire to purchase goods, repay debts and purchase assets. It volition also be determined by technology (greenbacks alternatives). Banks determine the amount of reserves that they concord by estimating how much they need for customer requests and for settling balances with other banks. Generally, other avails volition yield more than than reserves. The liquidity ratio is the ratio of reserves to bank deposits. Therefore, central bank cash is determined by the liquidity ratio, the cash demanded by households and the size of banking concern deposits. Subject area to the liquidity constraint (liquidity rate), commercial banks will create money past making loans when it is profitable to exercise then. This volition depend on the demand for loans, which is ready by the IS curve, and the funding costs set by the cardinal bank. Cash is less than 3% of a modern economic system. It is assumed that banking concern deposits do not pay interest and that households can agree either cash, deposits or authorities bonds. In reality we should also add corporate disinterestedness and corporate bonds as potential assets that households could buy.
The commercial bank money is determined by the size of electric current accounts. Households and firms determine the corporeality of cash that they volition hold. This will exist deponent on their income and the level of interest rates. As income increases, households will desire to deport more transactions and volition demand more than coin to exercise that; equally involvement rates ascension, the return on bonds becomes higher and makes banking concern deposits less bonny.
\[\frac{M^D}{P} = f(y, i, \Phi)\]
Where \(y\) is income, \(i\) is the nominal involvement rate and \(/phi\) is the structural changes that take place in the financial sector (such equally ATM machines). Given the Fisher equation \((i = r + \pi^E)\), if aggrandizement goes up, this adds to the opportunity cost of holding money and demand will fall. These private sector decisions in combination with the policy of the fundamental depository financial institution will set the amount of money. \(\Phi\) tin can likewise be used to capture things like a modify in confidence. In the period after 2008 when there was a loss of confidence in the financial organization, the demand for pure greenbacks increased. Fluctuations in the need for cash as a safe nugget hateful that the relationship betweeen coin and spending is non very stable.
The fiscal arrangement
The policy rate is the rate that the central banking company lends coin to the banking organisation. If there is payment on reserves, this provides the mechanism that keeps other curt-term interest rates shut to the policy rate. The reserve rate acts as a floor. It is the lending rate that determines demand in the economy (via the IS rate).
Commercial banks will face up a demand for loans and a cost of funds. They volition borrow from the money market if they exercise not have sufficient deposits. Information technology is causeless that banks are turn a profit-maximisers. Profits depend on: expected return on loans, toll of funds in the money market place and the opportunity price of bank upper-case letter. The expected return will exist affected by credit take a chance (even on secured loans). Bank hazard tolerance will vary and the power of the banking concern to acquit run a risk will depend on how much upper-case letter it has. The spread between the policy rate and the lending rate is determined by risk, adventure tolerance and capital. The involvement rate margin or banking mark-upwardly equation is
\[r = (1 + \mu^B)r^P\]
\(\mu^B\) is the banking mark-up that depends positively on risk and negatively on adventure tolerance and capital.
The policy rate and money market rates are more or less equal in normal conditions. The level of competition in the cyberbanking industry will also touch on the mark-upwardly of lending rates over policy rates in the medium term. The relatively low level of competition in the UK banking market is believed to make borrowing relatively expensive for Great britain borrowers with minimal alternatives forms of finance. (Kleimeier and Sander 2017) discover that level of comeptition is the almost important, but not the only influence on the extent that central bank involvement rate changes are passed through to other interest rates in the economic system. At that place are too debates about the relatinship between the level of competition and the stability of the financial system with some suggestions that more competition encourages more risky behaviour.
Credit constraints
Credit rationing is a primal characteristic of the banking system that stems from disproportionate data. This means that households face credit constraints. These credit constrains impact the slope of the IS curve and the power of the multiplier. It is hard for lenders to distinguish between bad luck and moral hazard. The more that borrowers use their own wealth to fund a project, the more confident the bank can be. The lender also has less precise information near future earnings. If a banking concern charges an boilerplate rate, there is a run a risk of adverse selection. Informational asymmetries mean that assets become very important and that people without avails will find themselves credit constrained. Positive role of banks: maturity transformation; aggregation (bringing together small savings into a usable amount); gamble pooling (default is a pocket-size part of the total).
Liqiudity run a risk
Banks face up liquidity risk. A depository financial institution run is a adventure in a fractional cyberbanking system. This has encouraged the development of lender of the last resort and eolith insurance. These schemes have to residue providing confidence and preventing moral gamble. Banks also face insolvency risk (nugget with less than liabilities). Equity owners, depositor and money-market partners will be affected. Solvency problems can crusade liquidity problems equally banks become cautious about lending to each other. In the 1930s the Federal Reserve was passive towards banking failure; in 2015 the primal banking concern learnt from the previous mistakes. However, in that location are limits. In Ireland the debts of the banking system were greater than the resource of the government. The relationship between the regime and the cardinal depository financial institution was highlighted during the European debt crisis of 2010.
References
Carlin, West., and D. Soskice. 2015. Macroeconomics: Institutioins, Instability, and the Financial System. 1st ed. OUP.
Kleimeier, Due south., and H. Sander. 2017. "Handbook of Competition in Banking and Finance." In, edited by J.A. Bikker and L. Spierdijk, 305–433. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Source: https://bookdown.org/robohay/economicsnotes/money-banking-and-the-financial-sector.html
0 Response to "Topic 6 Review Questions Money Banking and Financial Markets Answers"
Post a Comment